
Economic wrap-up for September 2023
Stats SA published a variety of reports, statistical releases and discussion documents in September. Here is a rundown of key economic indicators. GDP: SA invests in machinery & equipment and households cut back on spending In September, Stats SA released both national and provincial gross domestic product (GDP) figures. On the national front, GDP recorded read more »

EBA spending on transport increases in 2021/22
Extra-budgetary accounts and funds (EBAs) involved in the transport sector increased their spending in the 2021/22 fiscal year. However, despite the rise, expenditure is still below pre-pandemic levels. South Africa’s 256 EBAs are public institutions. They form an important arm of general government, responsible for delivering services to the public on behalf of government. Examples read more »

National government financial transfers: Who benefits the most?
One of the important tasks of national government is to redistribute funds, mainly received from taxes, to other sectors of the economy. These transfers serve a financial lifeline to diverse groups which includes households, public corporations, local and international organisations, and other levels of government. Key areas of spending On the revenue side, national government read more »

Government spending breaches R2 trillion
South African government spending broke the R2 trillion mark in the 2020/21 financial year. Large increases in expenditure were recorded for social protection, health, and general public services as the country battled the COVID-19 pandemic. At the same time, total revenue declined on the back of lower taxes received. The Financial statistics of consolidated general government read more »
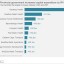
The public-sector: Shy on infrastructure investment
Data from 745 institutions provides an update on public-sector investment in infrastructure. A number of institutions pulled back on capital expenditure in 2021, while others increased their spending. Public-sector capital expenditure decreased by R6,1 billion (-3,0%) between 2020 and 2021, from R204,3 billion to R198,2 billion, representing the fifth consecutive year of decline. Capital expenditure represents money spent read more »

Provincial government finances: the impact of COVID-19
South Africa’s 122 provincial government departments spent R613,6 billion in 2020/21, according to the latest Financial statistics of provincial government statistical release. This is R16,9 billion more than the R596,8 billion recorded in 2019/20, representing a rise of 2,8%.1 The 2,8% rise is muted compared with the previous three years that recorded increases of around 7,0%. A closer read more »

Government finances: Social spending jumped in 2020/21
The 254 institutions known as extra-budgetary accounts and funds (EBAs) form an important arm of government. Financial data for 2020/21 (1 April to 31 March) show a sharp rise in EBA spending as government rushed to mitigate the impact of the pandemic. Much of the increase was on social benefits, mainly for the COVID-19 Temporary read more »
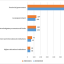
The impact of COVID-19 on national government finances in the 2020/2021 financial year
Total revenue collection of national government decreased by R95 billion from R1 385 billion in 2019/2020 to R1 290 billion in 2020/2021. The revenue streams in national government are taxes collected, grants and ‘other’ receipts (this comprises sales of goods and services and interest). Taxes collected contributed about 97% of total revenue. The decrease of read more »

Increase in number of out-of-school children and youth in SA in 2020
In 2021, close to 3% of 15-year-olds and nearly 9% of 17-year-olds dropped out of school. The General Household Survey, 2021, released by Statistics South Africa, indicates that although most 18- and 19-year-olds were still attending secondary school, almost three out of 10 pupils aged 18 years (29,3%) and 4 out of 9 (46,3%) of read more »

Money CAN buy happiness!
What is poverty and what does it mean to be poor? Does it mean not having enough money to meet basic needs including food, clothing and shelter? Does it mean not being able to afford to buy a car or furniture for your home or even go on holiday because your income does not read more »



